Embers of Innovation: A Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing in 2023
Related Articles: Embers of Innovation: A Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing in 2023
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Embers of Innovation: A Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing in 2023. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Embers of Innovation: A Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing in 2023

The digital landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by the insatiable demand for real-time data processing, low latency, and enhanced security. Traditional cloud computing, despite its vast capabilities, struggles to meet these burgeoning requirements. Enter edge computing, a transformative technology poised to redefine the way we interact with the digital world.
This comprehensive review delves into the intricacies of edge computing, exploring its core principles, applications, advantages, and challenges. By examining the latest advancements and industry trends, we aim to provide a clear understanding of how edge computing is shaping the future of technology and empowering businesses to unlock new opportunities.
Understanding the Edge: A Paradigm Shift in Computing
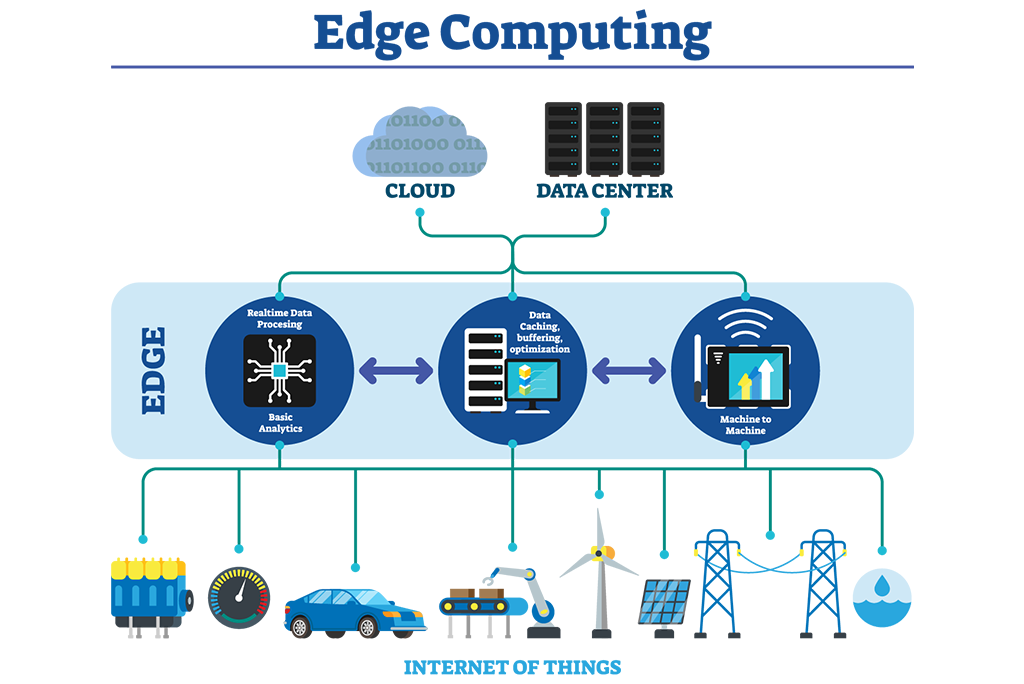
Edge computing, as its name suggests, shifts processing power closer to the source of data generation. This means data is processed and analyzed at the network’s edge, closer to users and devices, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud data centers. This fundamental shift in computing paradigm brings about a multitude of benefits, particularly in scenarios where latency is critical and data privacy is paramount.
The Pillars of Edge Computing:
- Decentralization: Edge computing decentralizes data processing, eliminating the need to transmit vast amounts of data to distant cloud servers. This reduces network congestion and minimizes latency, crucial for applications requiring real-time responses.
- Low Latency: By processing data locally, edge computing significantly reduces the time it takes for information to travel between devices and servers. This is particularly beneficial for applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and immersive gaming, where split-second decisions are critical.
- Enhanced Security: By keeping data closer to its source, edge computing mitigates security risks associated with data transmission over long distances. This is crucial for industries dealing with sensitive data, such as healthcare, finance, and government.
- Increased Bandwidth Efficiency: Edge computing reduces the strain on network bandwidth by processing data locally. This allows for more efficient use of existing network infrastructure and improves overall network performance.
Applications of Edge Computing: Transforming Industries
The versatility of edge computing has led to its widespread adoption across diverse sectors, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and interact with their customers.
1. Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing is a cornerstone of the burgeoning IoT ecosystem. By processing data at the edge, it empowers connected devices to make intelligent decisions autonomously, without relying on constant communication with centralized servers. This enables real-time insights, proactive maintenance, and enhanced user experiences.
2. Industrial Automation: Edge computing is transforming industrial processes by enabling real-time data analysis and control. This empowers manufacturers to optimize production lines, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency. Edge-enabled sensors and actuators allow for predictive maintenance, reducing costly equipment failures.
3. Autonomous Vehicles: The rise of autonomous vehicles is heavily reliant on edge computing. By processing data from sensors and cameras at the edge, self-driving cars can make real-time decisions about navigation, obstacle avoidance, and safety. The low latency of edge computing is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient autonomous driving.
4. Healthcare: Edge computing is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling real-time patient monitoring, remote diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans. Edge-enabled devices can collect and analyze patient data at the point of care, providing healthcare professionals with actionable insights for improved patient outcomes.
5. Retail: Edge computing is enhancing the customer experience in retail by enabling personalized recommendations, inventory management, and real-time pricing adjustments. Edge-powered devices can analyze customer behavior and preferences, providing tailored experiences that drive sales and loyalty.
6. Smart Cities: Edge computing is essential for building smart cities that are efficient, sustainable, and responsive to citizens’ needs. Edge-enabled sensors and devices can collect data on traffic flow, pollution levels, and energy consumption, allowing for real-time optimization of city infrastructure.
Benefits of Edge Computing: Unlocking New Possibilities
The adoption of edge computing brings about a range of benefits that extend across various industries and applications.
1. Reduced Latency: Edge computing minimizes the time it takes for data to travel between devices and servers, enabling real-time data processing and analysis. This is crucial for applications requiring immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and online gaming.
2. Enhanced Security: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing reduces the risk of data breaches and security vulnerabilities associated with data transmission over long distances. This is particularly important for industries handling sensitive data, such as healthcare, finance, and government.
3. Increased Bandwidth Efficiency: Edge computing reduces the strain on network bandwidth by processing data locally. This allows for more efficient use of existing network infrastructure and improves overall network performance.
4. Improved Scalability: Edge computing allows for flexible and scalable deployment of computing resources, enabling businesses to adapt to changing needs and accommodate increasing data volumes.
5. Cost Savings: Edge computing can reduce operating costs by minimizing data transmission and storage requirements. This can lead to significant savings in bandwidth, storage, and energy consumption.
6. Enhanced User Experience: Edge computing enables more personalized and responsive experiences for users, leading to increased satisfaction and engagement.
Challenges of Edge Computing: Navigating the Path Forward
While edge computing offers immense potential, it also presents a set of challenges that need to be addressed for its successful adoption and widespread implementation.
1. Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of data processed at the edge is paramount. Edge devices are often located in remote or less secure environments, making them vulnerable to attacks. Robust security measures, including encryption, access control, and threat detection, are crucial for safeguarding sensitive data.
2. Management and Orchestration: Managing and orchestrating a distributed network of edge devices can be complex. Businesses need to develop efficient systems for monitoring, updating, and managing edge devices, ensuring consistent performance and security across the network.
3. Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between edge devices, applications, and platforms is crucial for seamless data flow and integration. Industry-wide standards and protocols are needed to facilitate interoperability and prevent fragmentation of the edge ecosystem.
4. Power Consumption: Edge devices often operate in remote locations with limited access to power. Energy-efficient designs and power management strategies are essential for sustainable edge deployments.
5. Skill Gap: The rapid growth of edge computing has created a significant skills gap. Businesses need to invest in training and development programs to equip their workforce with the necessary skills to design, deploy, and manage edge solutions.
FAQs on Edge Computing:
1. What is the difference between edge computing and cloud computing?
Edge computing processes data closer to the source, while cloud computing relies on centralized data centers. Edge computing is ideal for applications requiring low latency, real-time data processing, and enhanced security.
2. How secure is edge computing?
Edge computing can be highly secure, but it requires robust security measures to protect data processed at the edge. Encryption, access control, and threat detection are essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
3. What are the key use cases for edge computing?
Edge computing is used in various industries, including IoT, industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, healthcare, retail, and smart cities. It is particularly beneficial for applications requiring low latency, real-time data processing, and enhanced security.
4. What are the challenges of implementing edge computing?
Challenges include security and privacy, management and orchestration, interoperability, power consumption, and the skills gap.
5. What is the future of edge computing?
The future of edge computing is bright, with continued advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various industries.
Tips for Implementing Edge Computing:
- Start with a clear business case: Identify specific use cases where edge computing can deliver tangible benefits.
- Choose the right hardware and software: Select edge devices and platforms that meet your specific requirements.
- Ensure robust security measures: Implement strong security protocols to protect data processed at the edge.
- Develop a comprehensive management strategy: Establish systems for monitoring, updating, and managing edge devices.
- Invest in training and development: Equip your workforce with the necessary skills to design, deploy, and manage edge solutions.
Conclusion: The Edge of Innovation
Edge computing is a transformative technology that is rapidly reshaping the digital landscape. By bringing processing power closer to the source of data generation, it unlocks new possibilities for real-time data analysis, low latency applications, and enhanced security. While challenges remain, the benefits of edge computing are undeniable. As businesses continue to embrace this innovative technology, we can expect to see a surge in groundbreaking applications that will revolutionize industries and empower individuals in unprecedented ways.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Embers of Innovation: A Comprehensive Review of Edge Computing in 2023. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!